What is a transformer? What is the working principle of the transformer?
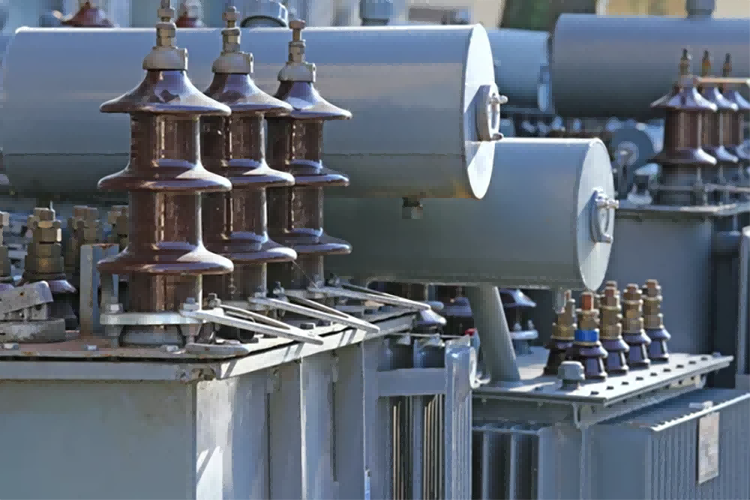
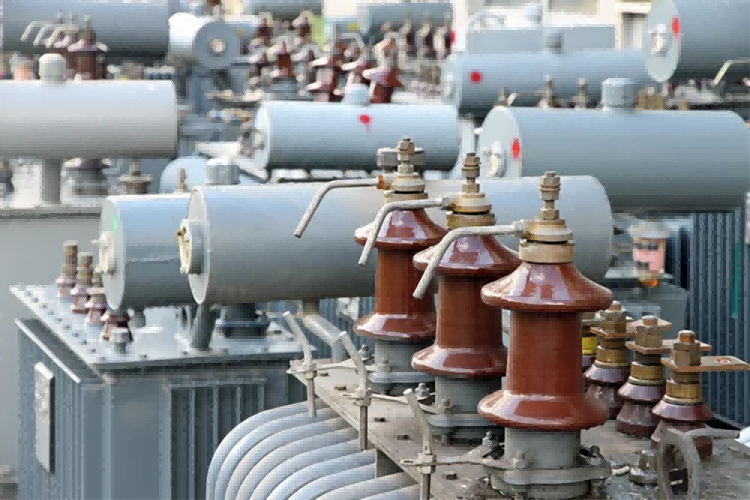
Transformer is a device that transforms AC voltage, current and impedance. When there is AC current in the primary coil, the iron core will produce AC magnetic flux (or magnetic core), so that the voltage (or current) is induced in the secondary coil. The transformer is composed of an iron core (or magnetic core) and a coil with two or more windings, in which the power supply winding is called the primary coil, and the remaining winding is called the secondary coil. In the generator, whether the coil motion is through the magnetic field or the magnetic field moves through the fixed coil, it can sense the potential in the coil. In these two cases, the value of the magnetic flux is unchanged, but the number of magnetic flux in the intersecting chain with the coil changes, which is the principle of mutual induction. Transformer is a kind of device that uses electromagnetic mutual sense effect, transform voltage, current and impedance.
The main components of the transformer are the primary coil, the secondary coil and the iron core (magnetic core). The main functions are: voltage conversion, current conversion, impedance conversion, isolation, voltage stabilization (magnetic saturation transformer) and so on.
Working principle of the transformer
The transformer is composed of an iron core (or magnetic core) and a coil with two or more windings, in which the power supply winding is called the primary coil, and the remaining winding is called the secondary coil. It can transform AC voltage, current, and impedance. The simplest core transformer is composed of a core made of a soft magnetic material and two coils with different turns on the core.
The function of the core is to strengthen the magnetic coupling between the two coils in order to reduce the iron vortex and hysteresis loss, the core is made of painted silicon steel sheets; there is no electric connection between the two coils, and the coil is made of insulated copper wire (or aluminum wire). One coil connected to the AC power supply is called the primary coil (or the original coil), and the other coil connected to the electrical appliance is called the secondary coil (or secondary coil). Actual transformer is very complex, inevitably exist copper loss (coil resistance heat), iron loss (iron core heat) and magnetic leakage (magnetic induction wire closed by air), etc., in order to simplify the discussion here only introduce ideal transformer ideal transformer established condition is: ignore the leakage flux, ignore the original, secondary coil resistance, ignore the loss of the core, ignore the empty current (the current in the original coil). For example, when the power transformer is running at full load (the secondary coil output rated power) is close to the ideal transformer situation.
Transformer classification
a.By cooling mode: dry-type (self-cooling) transformer, oil-immersed (self-cooling) transformer, fluoride (evaporative cooling) transformer.
b.According to moisture-proof classification: open transformer, sealed transformer, sealed transformer.
c.According to the core or coil structure classification: core type transformer (insert core, C type core, iron core), shell type transformer (insert core, C type core, iron core), ring transformer, metal foil transformer.
d.Classification by power supply phase: single-phase transformer, three-phase transformer, multi-phase transformer.
e.By use: power supply transformer, voltage regulating transformer, audio transformer, medium frequency transformer, high frequency transformer, pulse transformer.
Main function of the transformer
a.Energy transmission: the transformer can transmit electric energy from the original side circuit to the secondary side circuit to realize electric power transmission.
b.Voltage conversion: boost transformer can turn low voltage into high voltage for long distance transmission; step-down transformer can turn high voltage into low voltage to deliver electricity from the grid to the user.
c.Impedance exchange: the impedance of the original and secondary sides of the transformer can be different, that is, it has the impedance conversion function.
d.Current conversion: the current of the original side and the secondary side of the transformer can be different, that is, it has the function of current conversion, which can be both large and small, or from small to large.
e.Electrical isolation: the original side of the transformer and the secondary side of the circuit to achieve electrical isolation, only magnetic connection with each other, no power contact isolation transformer is a specific product.
f.phase shift: The simplest way to phase shifting is that the two windings are star shaped. When the angular connection is necessary, the phase shifting winding can also be set on the first side of the transformer. There are three ways to connect the phase shifting winding and the main winding, namely winding line, hexagon and Yanbian triangle.
g.Measurement: in the voltage, current, electric power measurement, the instrument transformer (i. e., voltage transformer, current transformer) is widely used in the accuracy of the instrument transformer directly affects the accuracy of the measurement.
h.Coupling: the transformer coupling has many applications in the electronic circuit, which can not only realize the signal transmission, but also has the function of isolation, to weaken or eliminate the interference.